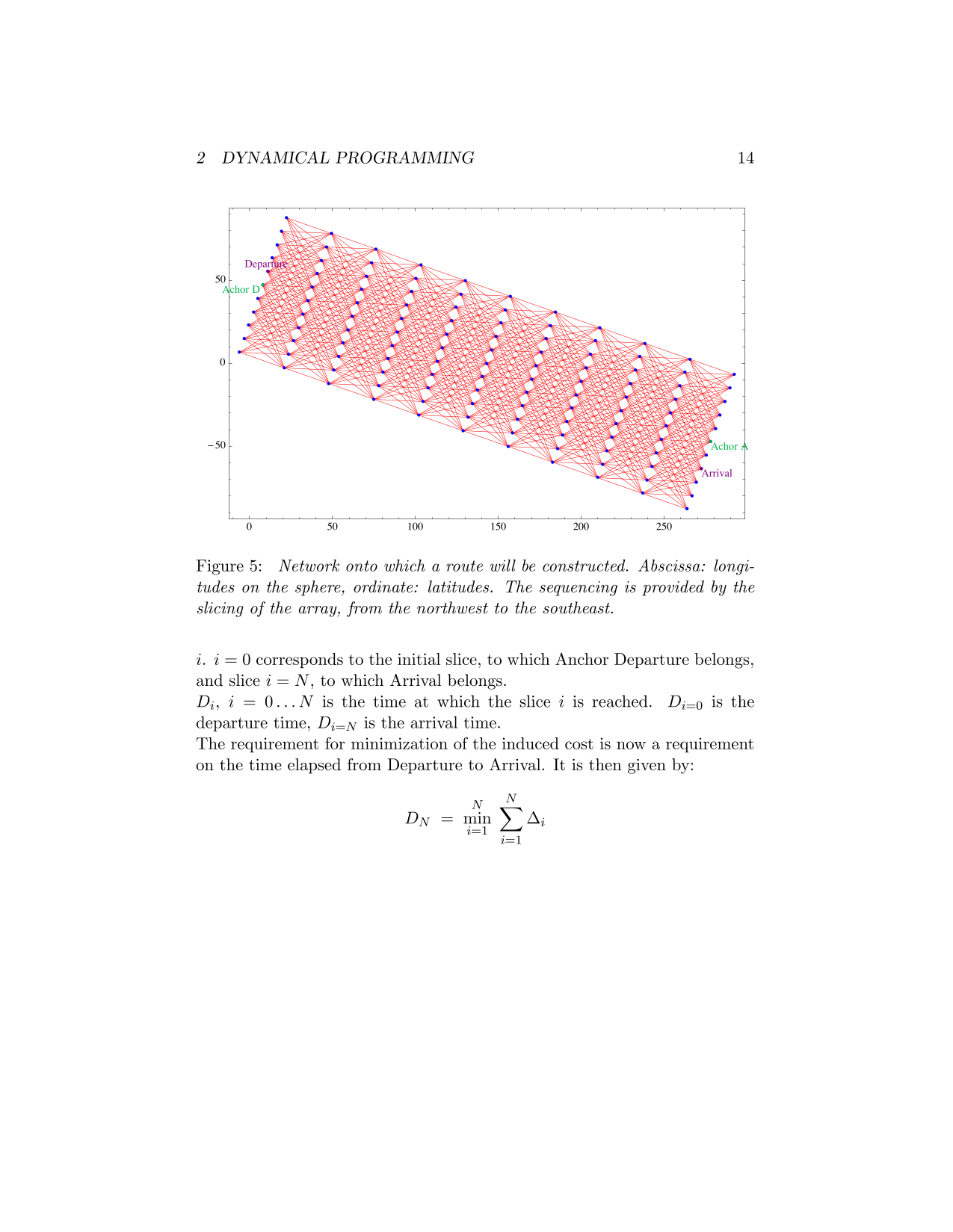
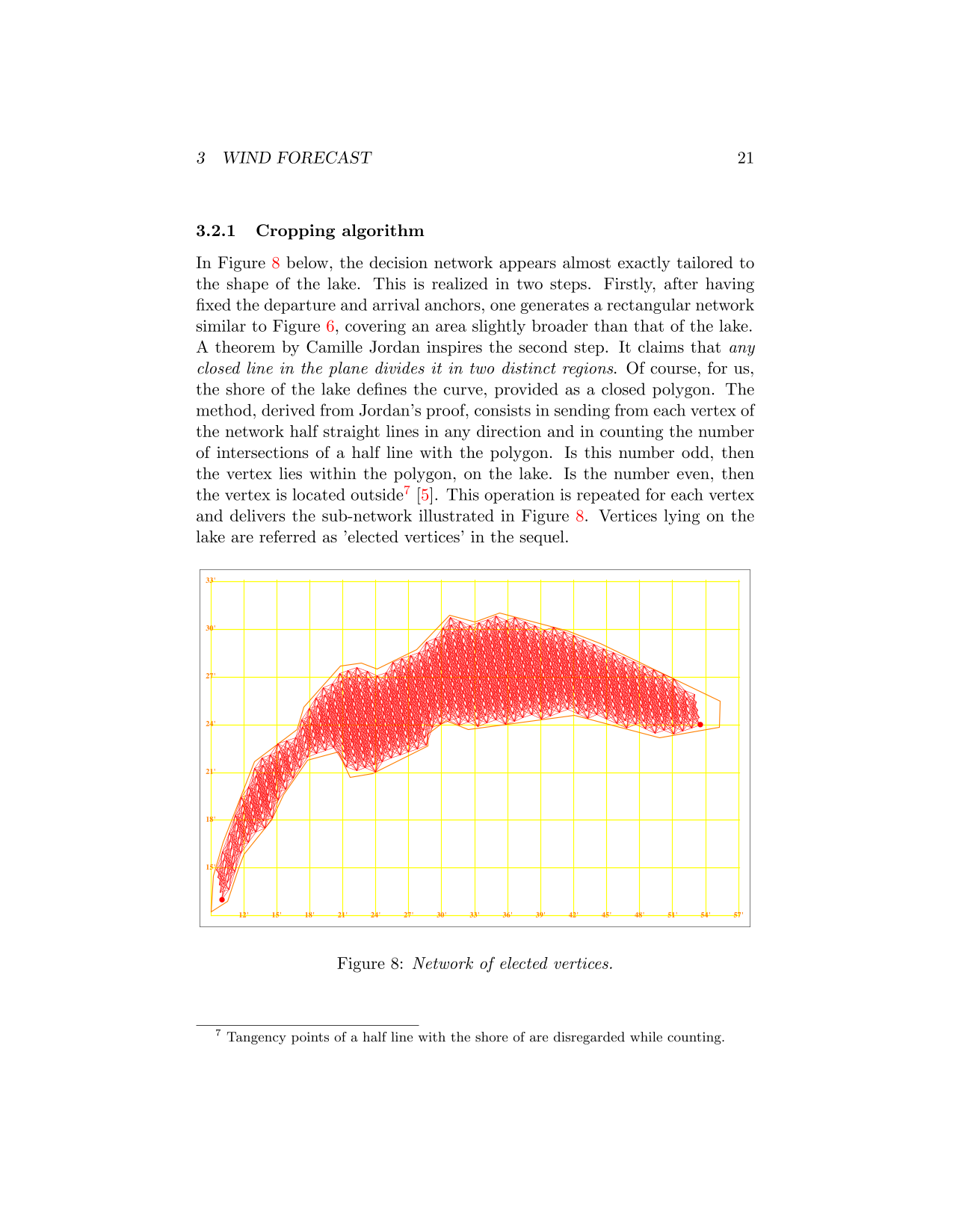
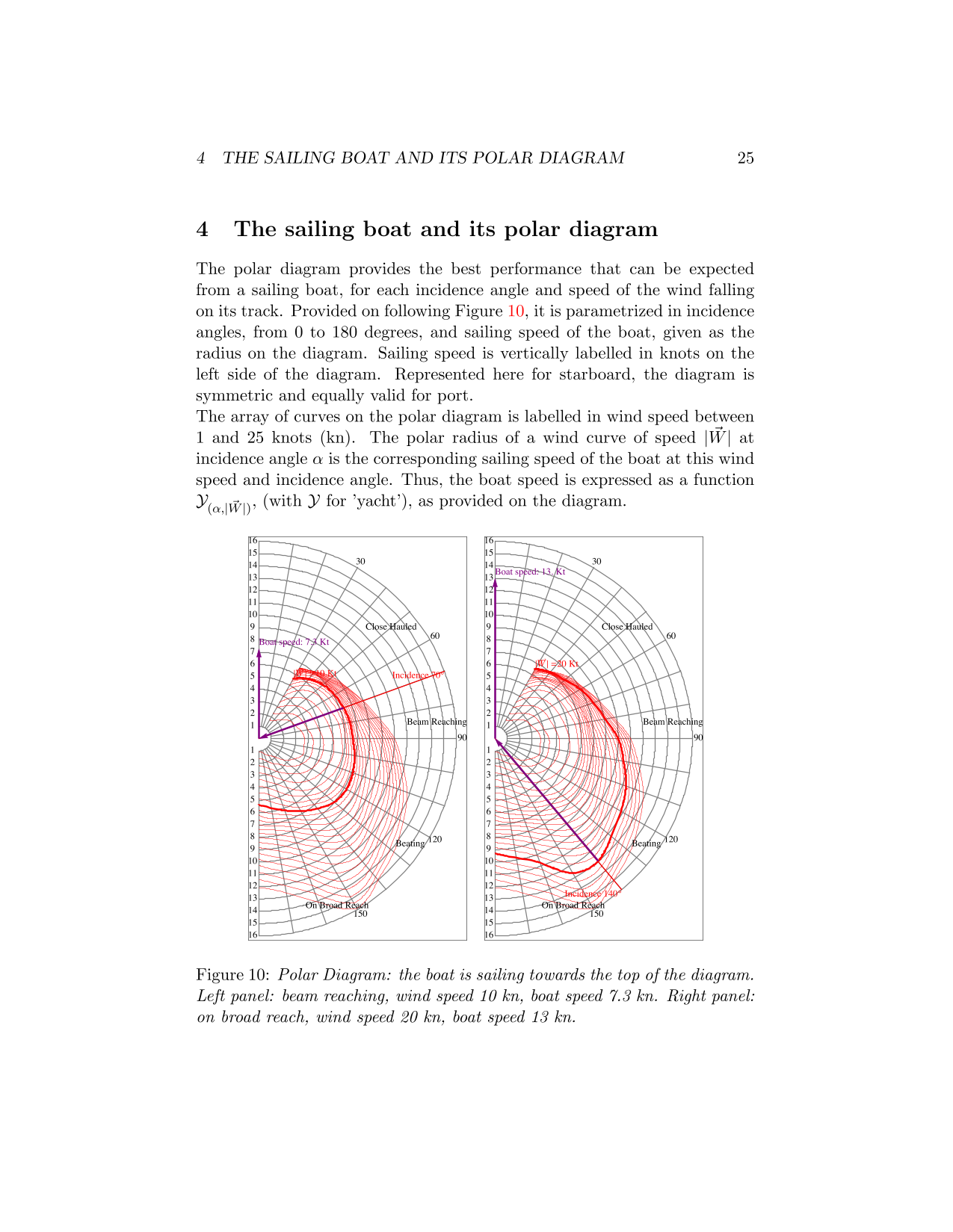
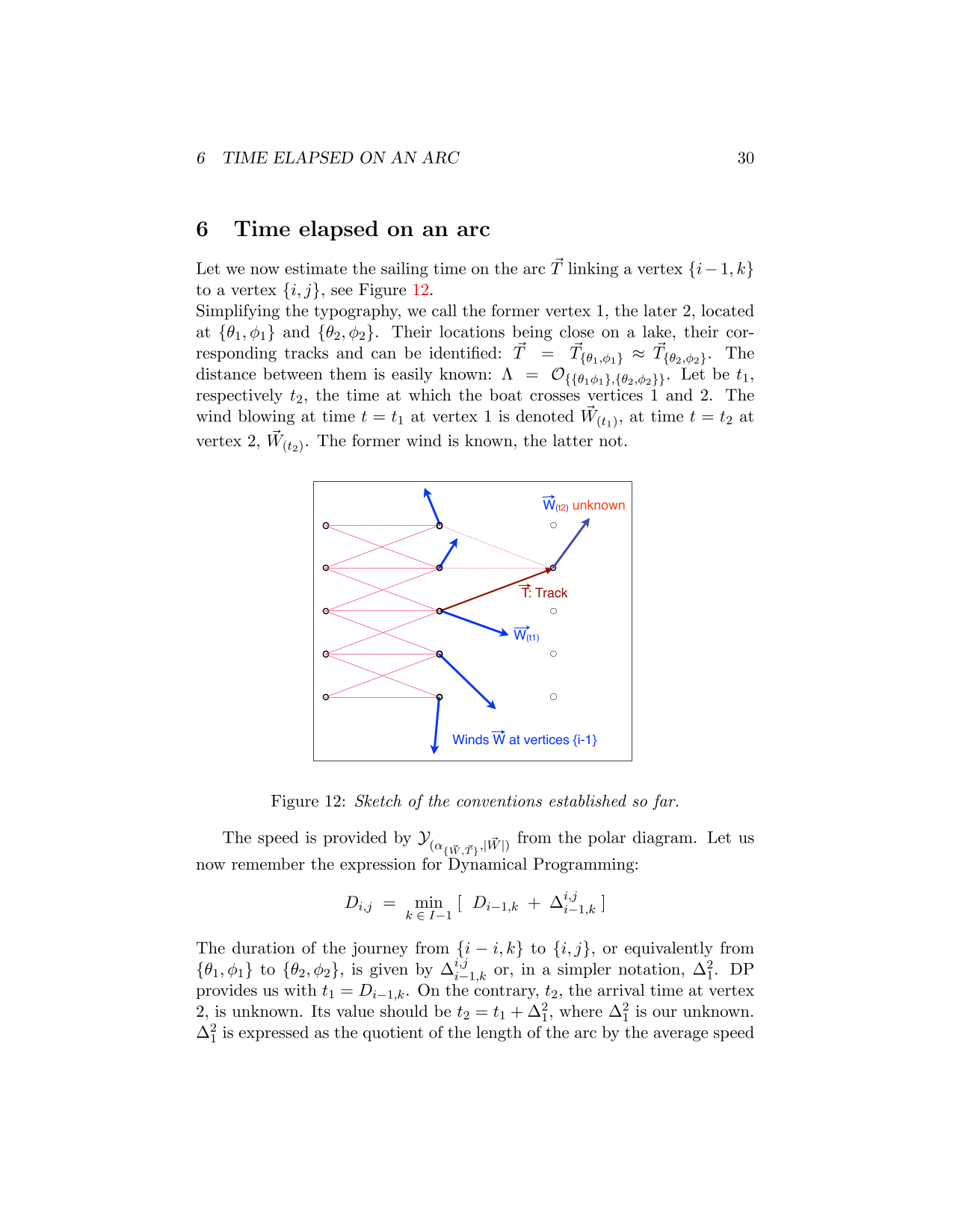
Optimal Routing
Old algorithms developed during the eigthies of the previous centuray aimed at computing optimal routes for boats sailing around the world are presented here. After the introduction of numerical weather systems operating at kilometric scale by the 2000's, I have refurbished these algorithms for lakes.




































The topic of routing experiences a second life as autonomous drones are developed for a vast array of activities. The following link provides such an example, developed at the Autonomous Systems Lab of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH Zurich).



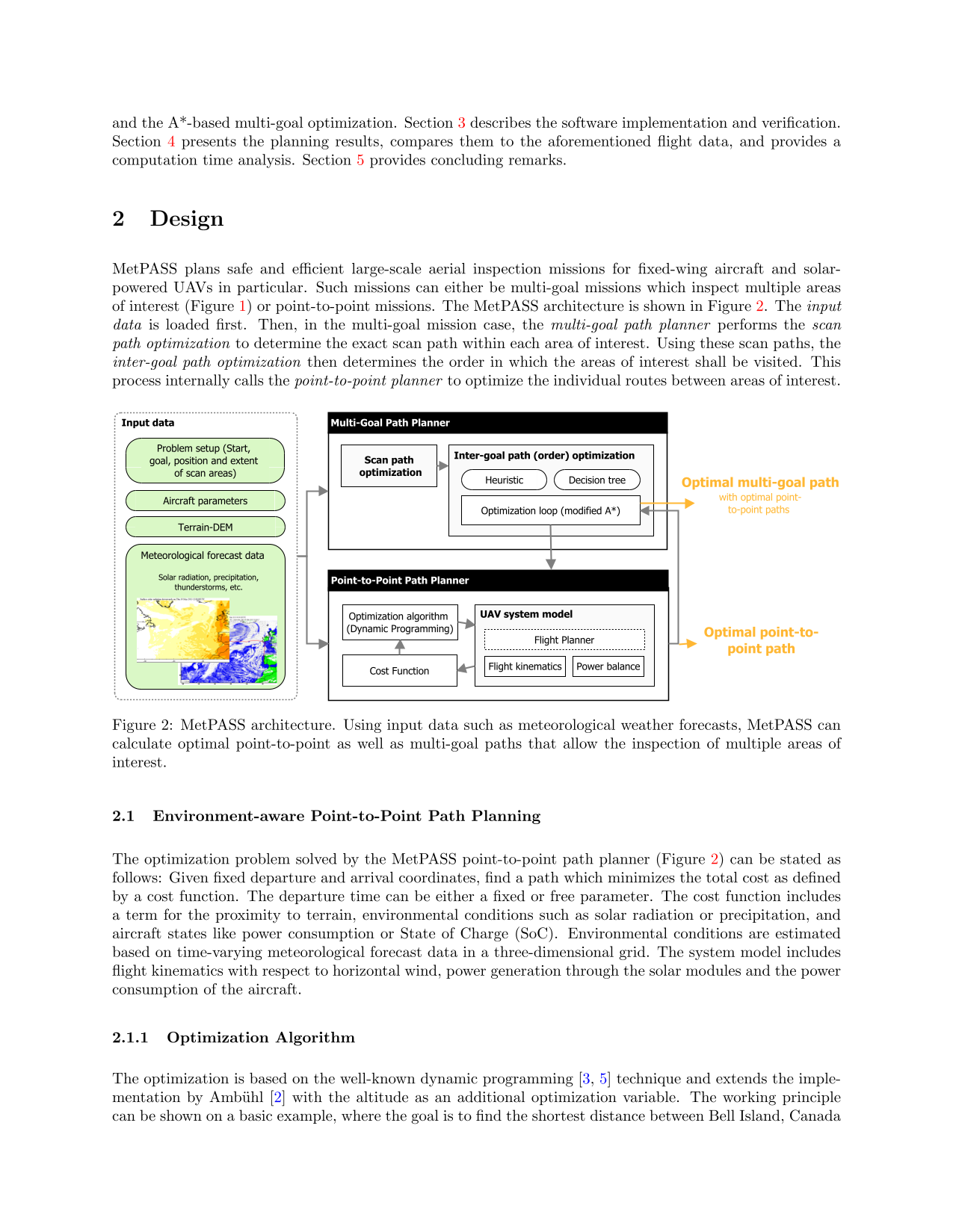






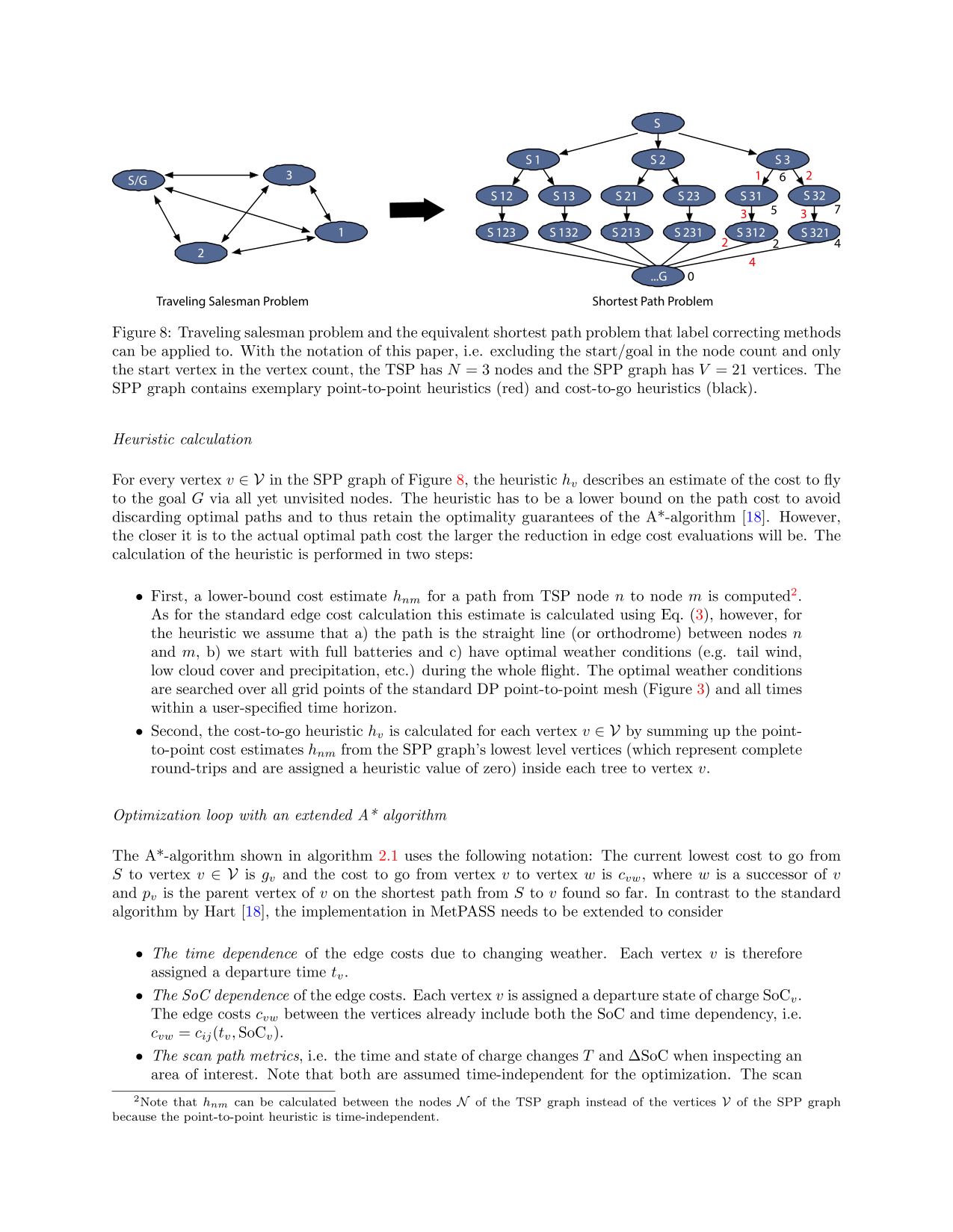



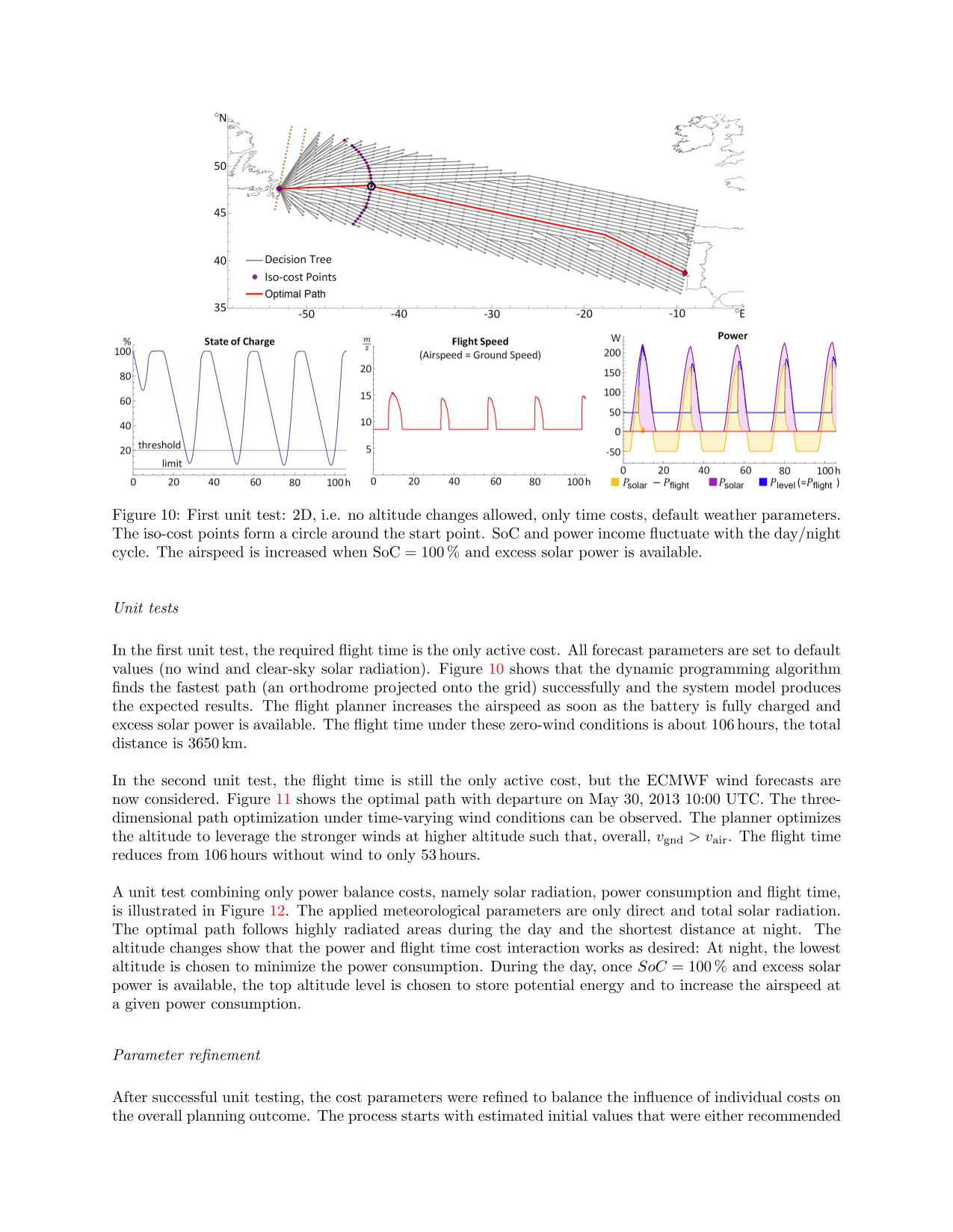






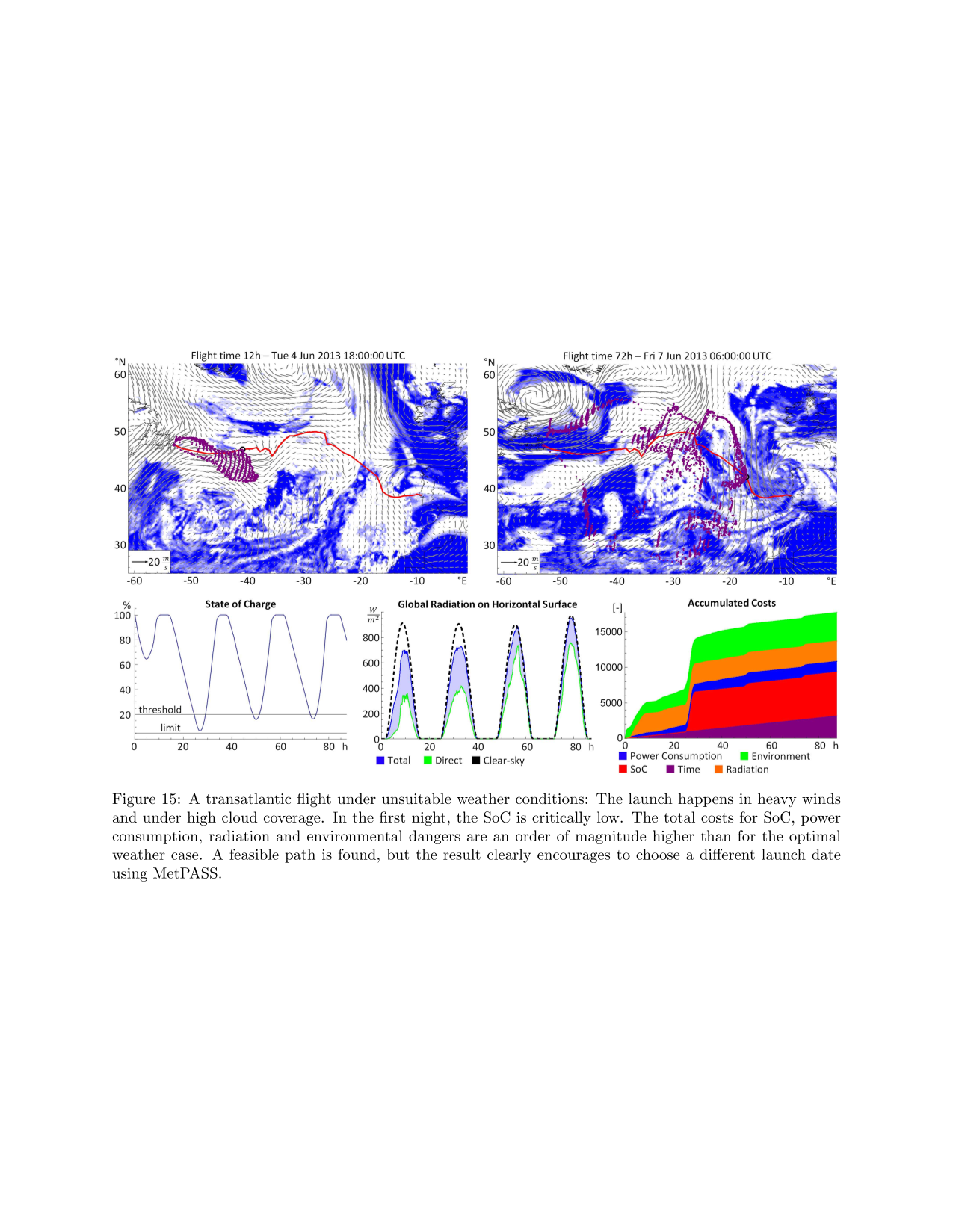











‘Solar-powered aircraft promise significantly increased flight endurance over conventional aircraft. Although this enables large-scale inspection missions, their fragility necessitates that adverse weather is avoided. This paper therefore presents MetPASS, the Meteorology-aware Trajectory Planning and Analysis Software for Solar-powered unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). MetPASS is the literature's first path planning framework that considers all safety- and performance-relevant aspects of solar flight: It avoids terrain collisions and no-fly zones, integrates global weather data (sun radiation, wind, gusts, humidity, rain, and thunderstorms), and features a comprehensive energetic model to avoid system risks such as low battery charge. MetPASS leverages dynamic programming and an A*-search-algorithm with a custom cost function and heuristic to plan globally optimal point-to-point or multi-goal paths with coverage guarantees. A full software implementation is provided. The planning results are analyzed using missions of ETH Zurich's AtlantikSolar UAV: an 81 h stationkeeping flight, a hypothetical 4000 km Atlantic crossing, and two multiglacier inspection missions above the Arctic Ocean. It is shown that integrating meteorological data is indispensable for reliable large-scale solar aircraft operations. For example, the nominal no-wind flight time of 106 h across the Atlantic is reduced to 52 h by selecting the correct launch date and flight path.’
